What are gallstones?
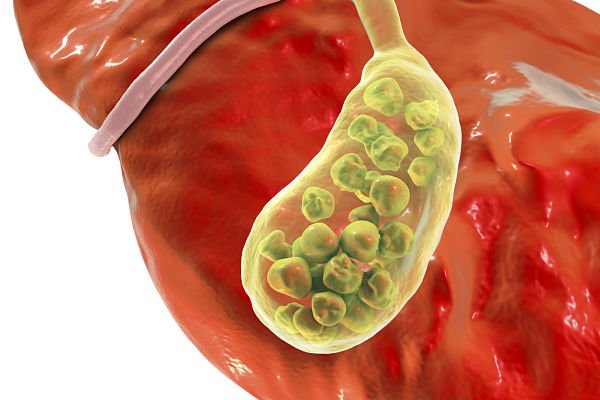
Gall is an old fashioned word for bile which is a substance produced by the liver and stored by the gall bladder before being emptied along the bile duct to mix with recently eaten food in your duodenum where it is digested.
A dark green to yellow brown liquid, bile is made up of a surprising number of chemical including cholesterol, amino acids and electrolytes and we produce between 400 to 800 ml a day.
Types of gallstone
Gallstones occur when bile becomes crystallised and causes an obstruction in the bile duct. This happens in around 10%-15% of Europeans but often without any apparent symptoms. In this instance they are called silent stones.
There are three types of gallstone:
- Cholesterol stones – where the stone comprises more than 80% These are the most common. Cholesterol stones are yellow, green, brown or white, around 2.5cm big and with a central dark spot.
- Pigment stones – where the stone comprises less than 20% cholesterol - are mostly made up of bilirubin, calcium and bile salts. These ted to be small, black and numerous and are the least common.
- Mixed stones – which are made up of between 20% and 80% cholesterol as well as the chemicals which are also seen in pigment stones
The size of a gallstone can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball.
Why might you get gallstones?
These typically occur in people near or above 40 years of age and especially in women before menopause.
Increased risks generally come down lifestyle such as being sedentary or obese; or diet such as eating a high fat, high cholesterol or low fibre diet.
Pregnancy can increase risk, as can taking medications which include oestrogen such as contraceptives or hormone therapy drugs.
Gallstones can also run in families and are associated with conditions such as diabetes or blood disorders
Usual symptoms and diagnosis
If your gallstones are not silent you may notice the following signs or symptoms:
- A sudden onset of quickly increasing pain in the centre or upper right of your abdomen or just below your breastbone. These may last hours at a time and come in waves
- Referred pain in your shoulder blades or right shoulder
- Nausea or vomiting
You need to quickly seek medical advice if you develop:
- Intense pain which means you cannot comfortably sit or stand
- Yellowing of your eyes or skin (this is caused by jaundice)
- A high fever with chills
Diagnosis will require blood tests and ultrasound. MRI or CT scans are likely to be used if the ultrasound results are inconclusive.
Treatment
Gallstones will naturally pass through the body, so if there are no symptoms or one incident treatment may actually be unnecessary
Keyhole surgery will be carried out if all the gallstones are situated within the gall bladder. Some people may require ERCP treatment which uses an endoscope.
I hope this has been helpful. Please get in touch if this has raised any concerns.
We make every effort to ensure that all health advice on this website is accurate and up to date. However it is for information purposes and should not replace a visit to your doctor or health care professional. As the advice is general in nature rather than specific to individuals we cannot accept any liability for actions arising from its use nor can we be held responsible for the content of any pages referenced by an external link.
